Vouch LSD Protool
The Vouch LSD Protool is comprised of several components which facilitate:
- Creating of (minting) the vPLS Liquid Staking Token (LST)
- Control user and node deposits
- Handle rewards distributions
- Monitor and mediate Validator Nodes.
Smart Contracts
The core part of Vouch LSD Protool is a set of smart contracts.
Core contracts:
- vPLS: an PRC-20 compatible derived token. Users receive this token when depositing PLS to UserDeposit and burn it when unstaking.
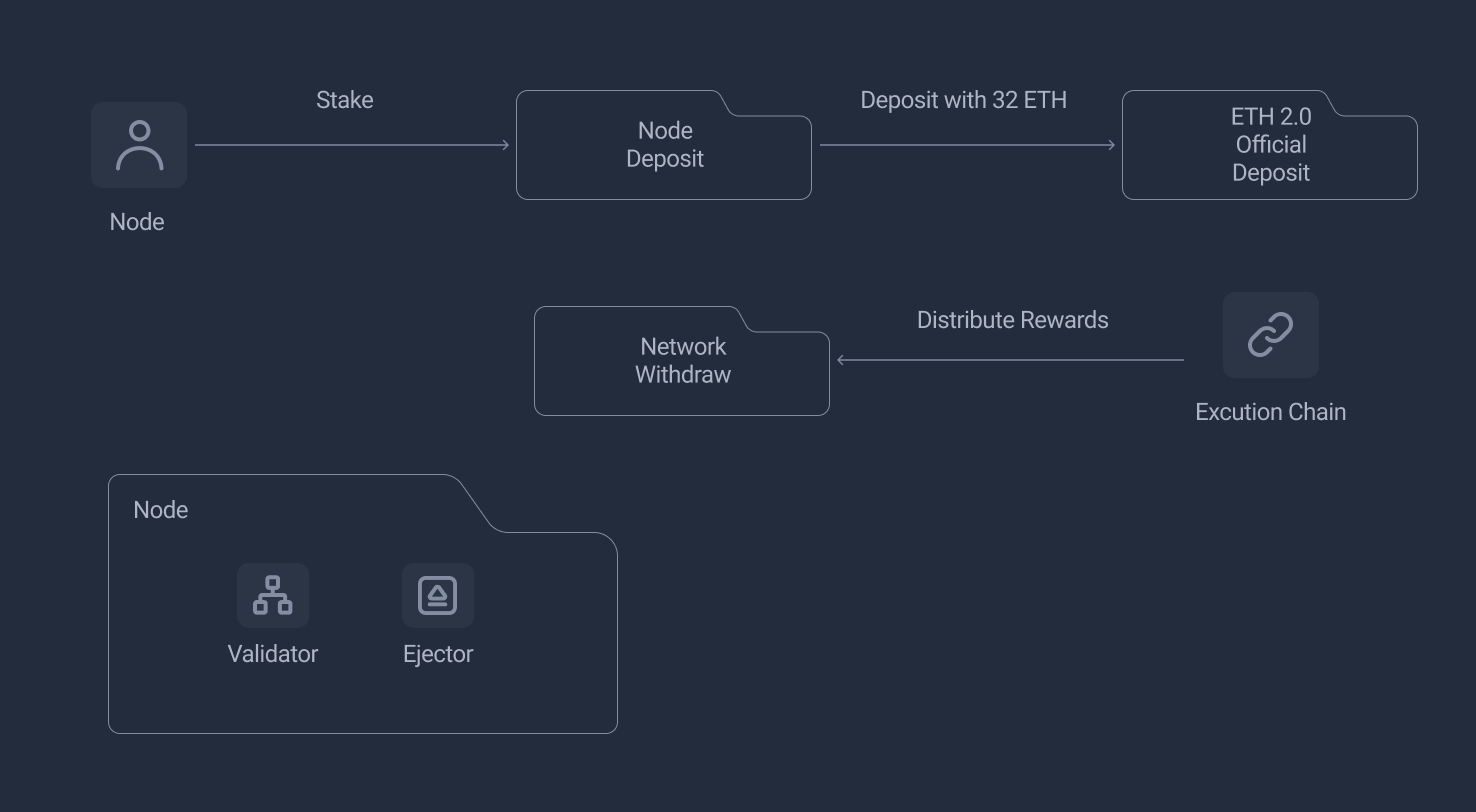
- NodeDeposit: register node and call PLS official deposit contract
- UserDeposit: a pool user deposits in, will be used by node
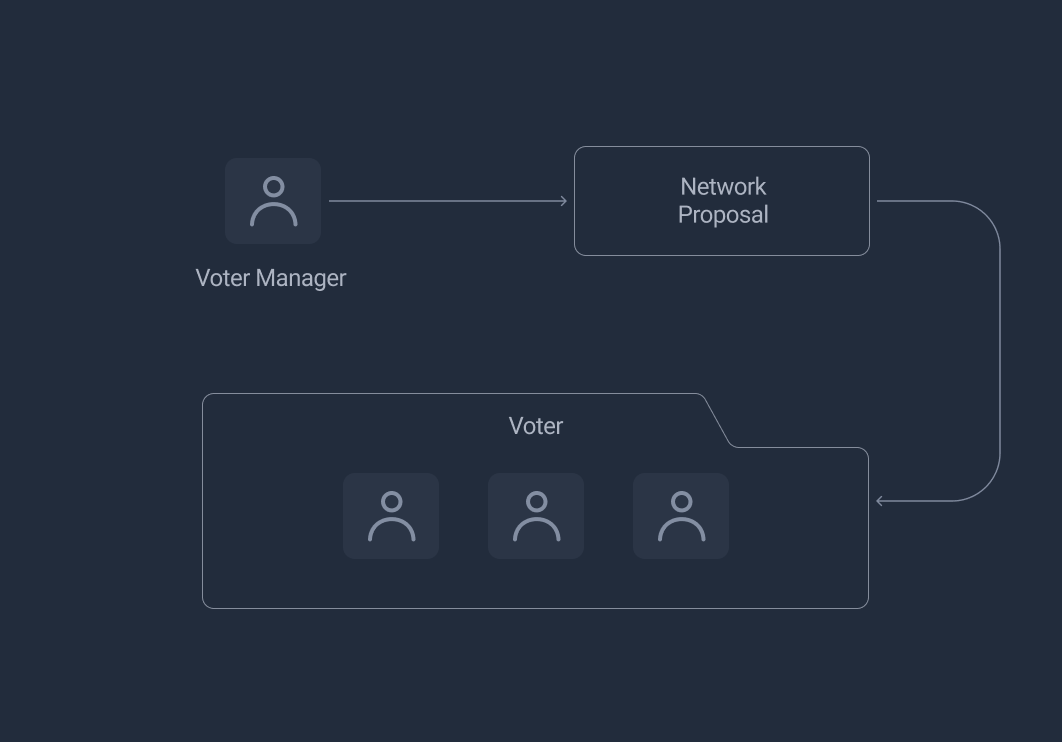
- NetworkProposal: voters submit proposal and execute corresponding action
- NetworkWithdraw: distribute rewards to parties
Core roles:
- Voter: privileged to propose changes to the on-chain status
- Node: an account which manages its validators and receives rewards
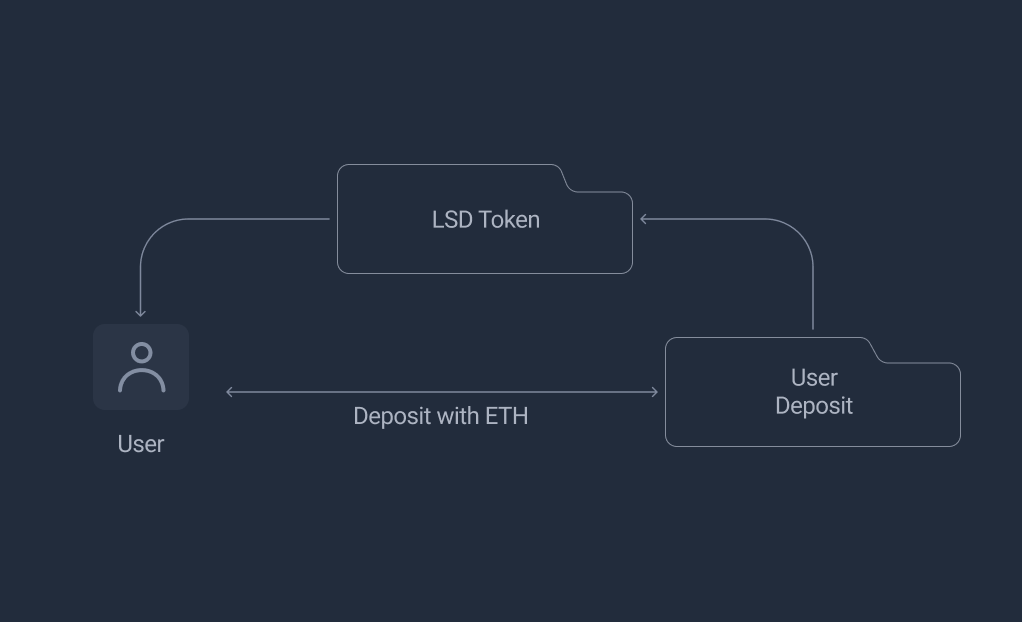
User Deposit Flow
UserDeposit contract manages all users' deposited PLS and returns the vPLS Token. When new users deposit into the pool, it provides a "float" balance which can be used as liquidity for other users wishing to exit. Primarily the pool is used node staking and will be matched with available Pulsechain Nodes.
amountLsdToken = TotalSupplyLsdToken / TotalNetworkPLSBalanceOfUsers * amountPLS
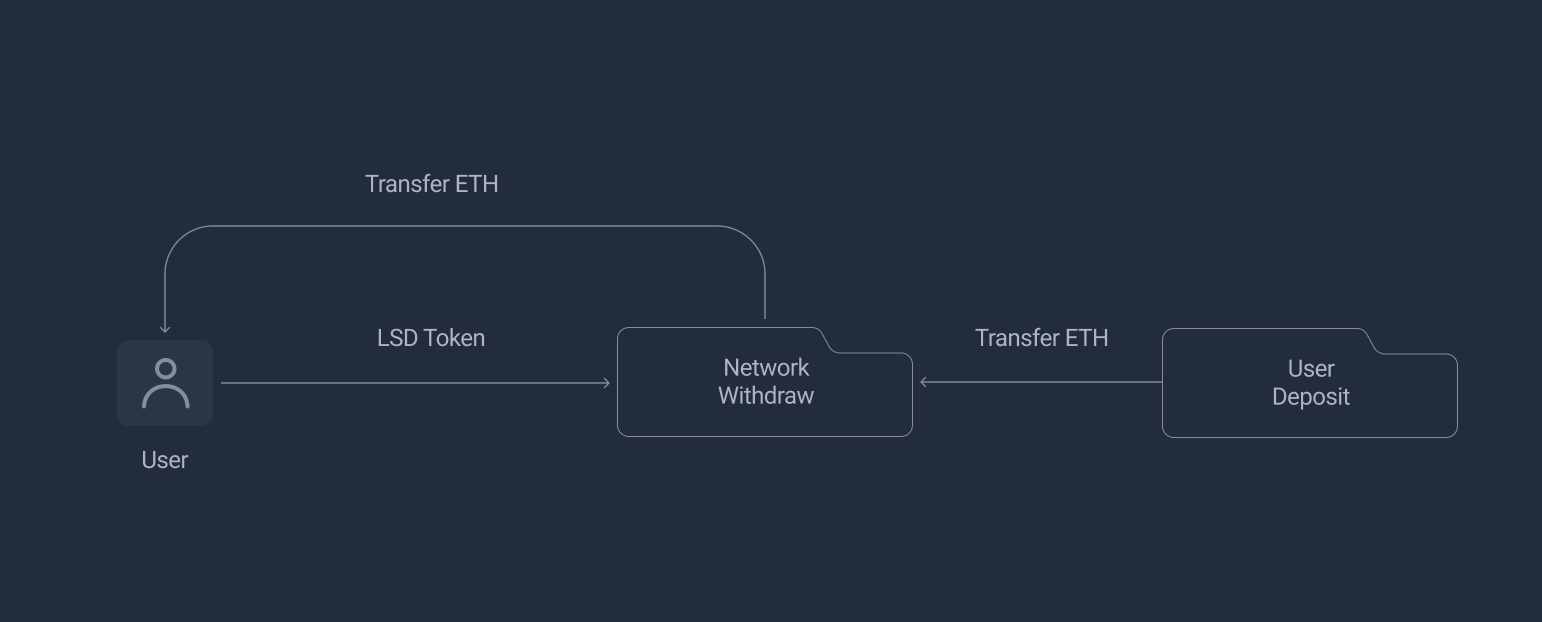
User Unstake Flow
Any vPLS holder is a valid user, and can call NetworkWithdraw to change (redeem) PLS with vPLS.
PLS will be transferred to the user instantly if the network pool has sufficent balance.
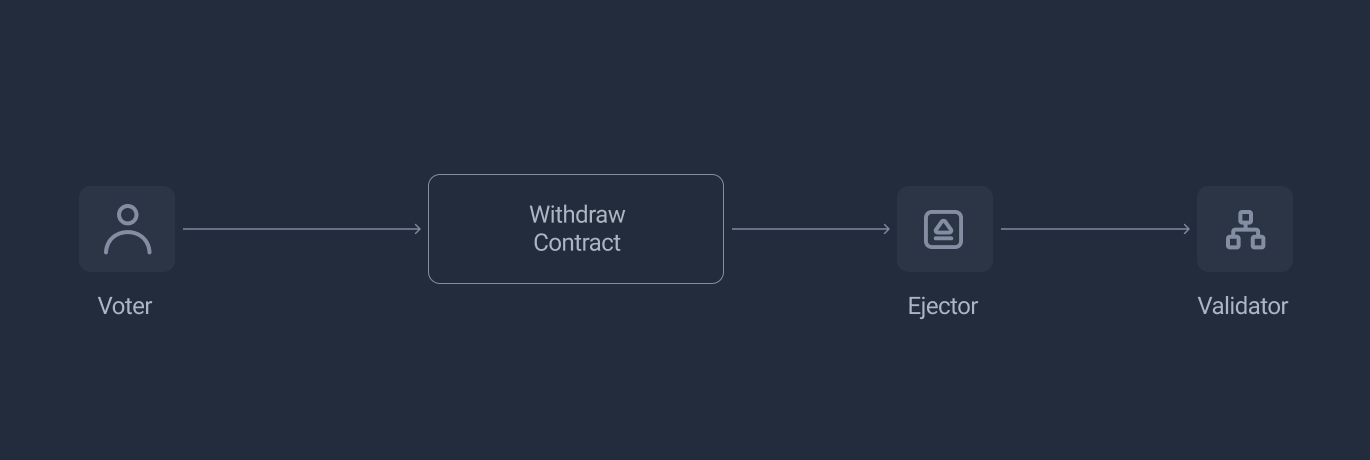
If it does not have enough PLS balance for any users, voters will select a batch of validators to exit, then users would call withdraw specifically to receive PLS when NetworkWithdraw satisfies the request by exiting the required validators.
Node Deposit Flow
Node providers will be served by individuals or single entities who are responsible for the consistency, security, availability and activity of the validator. They will be slashed if the validator is not working as expected.
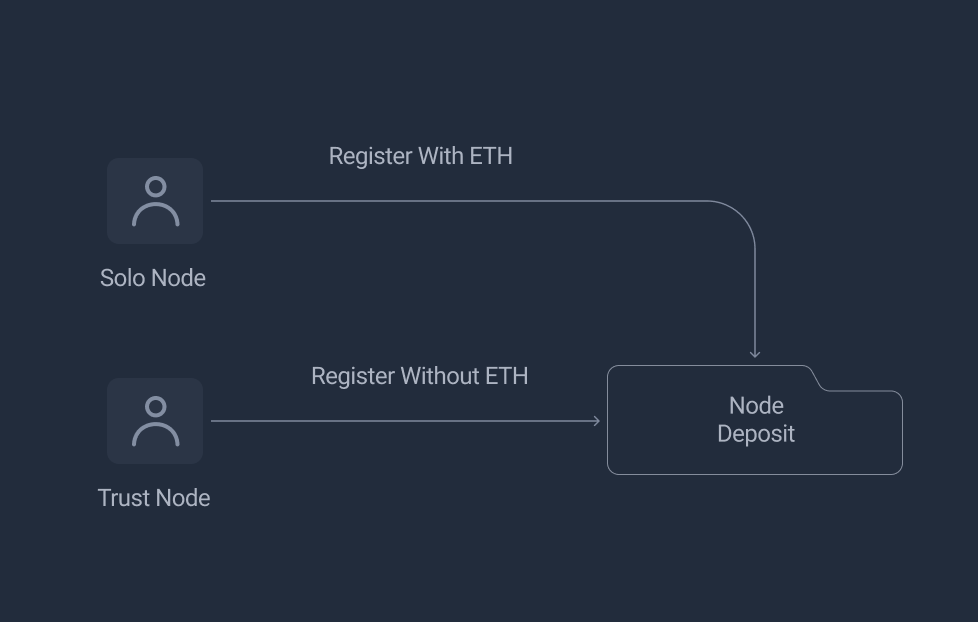
The NodeDeposit contract provides interfaces for node providers to deposit and stake to register validators. According to whether PLS is needed at the depositing phase, it can be separated into solo nodes and trust nodes.
The NetworkWithdraw contract will be used as the Withdrawal Credentials when depositing in the PLS official stake contract. This ensures the PLS LSD Stack maintains full custody over staking rewards, and misbehaving validators can have exit balances adjusted accordingly.
Solo Node
Unlike normal stakers which are required to put 32 Mil PLS up for deposit to create a new validator, each solo validator only need to deposit 12 Mil PLS. This will be coupled with 20 Mil PLS borrowed from the user deposit pool to create a new validator.
Trust Node
Trust Node providers don't need to deposit any PLS and still can run a validator. All the required 32 Mil PLS deposit requirement is provided by user deposit pool. Trusted nodes provide a way for the system to ensure deposited PLS is used in an effcient manner and earning maximum yield. They can be easily added and exited as the User Pool requires.
Node Stake Flow
When a node calls the stake function in NodeDeposit, the requried amount of 32 Mil PLS will be deposited to official deposit contract, all node operators should run a validator and an ejector service. After the validator has been activated on the Beacon chain, rewards will distribute to NetworkWithdraw automatically.
Node Claim Flow
At regular intervals, voters will flag a checkpoint on the network. Currently, checkpoints occur approx every 8 hours (90 epochs).
At a new checkpoint, the voters will collectively create a true snapshot of the state of the node operators in the project network, which it will use to determine deposit and reward PLS for each validator provider during that interval. This information is compiled into a Merkle Tree. The Merkle Tree is built into a formatted data (json file) and hosted on a Decentralized Data Storage (DDS) network such as ipfs or arweave.
Once the tree is submitted, voters will submit the merkle root of this checkpoint in NetworkWithdraw, then node providers are able to claim their rewards in PLS with proof by calling the contract.

Relays
Relays, the essential off-chain service component, are responsible for administrative duties required by the protocol that cannot be achieved by smart contracts due to technical limitations of the Pulsechain Network. They will update crucial network parameters in the PLS LSD smart contracts.
Calculate network balances
At a certain interval, currently 24 hours (270 epochs), the voters will update the validator's balance to calculate network staking and priorty fee (tip) rewards, distribute it to the platform, node providers, and users. The rate (ratio) between vPLS and PLS will be updated as well.
Slash mechanism
Voters will provide a validator slash detection mechanism to measure a validator's running status and decide which solo node or trust nodes are not operating in an effecient manner. Poor performing nodes will attract the appropriate penalties, these penalties will be recycled to UserDeposit contract to ensure User Deposits are protected.
Withdrawal Credential Match Check
Voters will additionally check each node provider's withdrawal_credentials to ensure the PLS LSD stack will successfully receive the validators' rewards which it will in turn distribute accordingly.
Manage Voters
Considering voters' significant role in the whole system, the correctness and availability of voters must be guaranteed by protocol design. So the introduced voter manager role will add and remove voters when it detects dishonesty.
After initialization of the system, there will be a group of voters designated as standby voters, their accounts are stored in the NetworkProposal contract. For each contract function which requires off-chain data, we will get the voters' account from NetworkProposal and check whether the msg.sender is a voter or not. The data which is written on-chain requires 2/3 voters agreements. In the meantime, a minority of voters who submit faulty data will be marked as suspicious. If they continue submitting faulty data, they will be expelled.
Node Ejector
Each node operator is require to run this Ejector component (software) which allows validators to be gracefully exited as required. Voters will select a batch of validators to enter the exit process, when user pool does not satisfy the user unstake amount requested.